A Practical Guide to Automated GUI Tests
Automated GUI tests are basically scripts that pretend to be a user. They simulate all the clicks, scrolls, and typing you'd expect a real person to do, all to make sure an application's graphical user interface (GUI) is working correctly. Think of it as a tireless robot that repeatedly pokes and prods every visual element—buttons, menus, forms—to ensure nothing breaks after a code change. It's a crucial process for catching bugs early and keeping the user experience smooth.
Unpacking the Role of Automated GUI Testing
At its heart, the GUI is the bridge between your software and your user. It’s the visual landscape where they interact with your product, form impressions, and hopefully find value. If that bridge is shaky—with unresponsive buttons, broken layouts, or confusing navigation—the user's journey grinds to a halt.
Automated GUI tests are the quality inspectors for this bridge. They make sure it stays sturdy, reliable, and easy to cross, no matter what changes are happening underneath. This kind of testing goes beyond just checking the underlying code logic; it’s all about seeing the application from the user's perspective. The goal is simple: confirm that what the user sees and interacts with behaves exactly as it should, across every device and browser.
The Core Purpose of GUI Automation
Automated GUI tests are all about answering critical questions about the user experience before your customers ever have to. This validation is a cornerstone of any mature software quality assurance strategy.
So, what are we trying to achieve here?
- Verifying Functionality: Does clicking the "Submit" button actually submit the form? Does that dropdown menu show the right options?
- Ensuring Visual Consistency: Are fonts, colors, and spacing correct on every page and at different screen sizes?
- Validating User Workflows: Can a user actually sign up, make a purchase, or complete any other multi-step process without hitting a wall?
By automating these checks, teams create a safety net that catches regressions—those pesky bugs where new code breaks something that used to work perfectly. This frees up human testers to focus on the more complex, creative, and intuitive exploratory testing that machines just can't handle.
The demand for this kind of quality check is exploding. The global automated software testing market, currently valued at USD 84.71 billion, is projected to hit USD 284.73 billion by 2032. That’s a massive jump, and it speaks volumes about the growing complexity of modern applications and the absolute need for fast, reliable validation.
Ultimately, automated GUI testing isn't just a technical checkbox. It's a commitment to quality. It ensures that every release makes the user experience better, not worse, helping to protect your brand's reputation and keep customers happy in a ridiculously competitive market.
The Strategic Benefits of GUI Test Automation

Let's be honest: setting up automated GUI tests takes some upfront effort. It's an investment of time and resources. But the payoff? It’s huge. You’re not just catching bugs; you’re fundamentally changing how your team builds and ships software. Quality assurance shifts from being a simple cost center to a strategic engine that drives real business value.
The industry is already voting with its dollars. The global automation testing market was valued at a whopping USD 25.43 billion in 2022 and is on track to hit USD 92.45 billion by 2030. This isn't just a trend; it's a direct response to the demands of Agile and DevOps, where getting reliable software out the door fast is the name of the game.
Radically Expand Test Coverage
Think about manual testing for a second. A QA engineer can only test so many device and browser combinations in a single day. It's humanly impossible to cover everything, which often means we stick to the "happy path"—the most common user journeys.
This is where automation completely changes the game. Automated tests don't get tired and can run in parallel, 24/7. This allows you to:
- Test Across Hundreds of Environments: Check your app's look and feel on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Windows, macOS, and countless screen resolutions—all at the same time.
- Validate Complex User Scenarios: Run through intricate workflows with huge data sets that would be a nightmare for a human to test repeatedly and accurately.
- Cover All the Weird Edge Cases: Systematically poke and prod at those uncommon but critical interactions that often get missed in the rush to release.
The result is a consistent, high-quality experience for every single user, no matter how they access your application.
Accelerate Release Cycles and Improve Velocity
In a manual-only world, regression testing is the ultimate bottleneck. Every time a new feature is added, the team has to stop and painstakingly re-test everything to make sure nothing broke. This can take days, grinding the entire release pipeline to a halt.
Automated GUI tests turn this bottleneck into an accelerator. When you weave them into your CI/CD pipeline, they act as an instant quality gate. Developers get feedback in minutes, not days, letting them catch and fix regressions before they become a real problem.
This constant feedback loop builds confidence and empowers your team to ship better software, faster. The efficiency boost isn't just about speed; it's also about the bottom line. This approach is a cornerstone of achieving long-term savings and efficiency in software development and a better ROI.
Manual vs Automated GUI Testing At a Glance
To put it all into perspective, let’s look at a direct comparison. It quickly becomes clear why automation is a game-changer for modern development teams.
| Aspect | Manual GUI Testing | Automated GUI Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow and time-consuming, a major bottleneck. | Extremely fast, can run in parallel 24/7. |
| Coverage | Limited by human capacity; often just "happy path." | Extensive; covers countless browsers, devices, and edge cases. |
| Accuracy | Prone to human error, inconsistency, and missed steps. | 100% consistent and repeatable, eliminates human error. |
| Cost | High long-term cost due to repetitive manual labor. | Higher initial setup cost, but significant long-term ROI. |
| Scalability | Scales poorly; more tests require more people. | Highly scalable; add more tests without adding more people. |
| Team Focus | QA engineers are stuck doing repetitive, monotonous tasks. | Frees up QA to focus on high-value exploratory testing. |
The table makes the practical differences starkly clear. Automation isn’t about replacing humans; it’s about enabling them to do their best work.
Enhance Accuracy and Empower Your Team
Let's face it, humans make mistakes. Especially when doing the same mind-numbing tasks over and over. A manual tester might accidentally skip a step, type in the wrong data, or just have an off day. These small slip-ups lead to inconsistent results and bugs slipping through the cracks.
Automated scripts, on the other hand, are robots. They follow the exact same steps with perfect precision every single time. This ruthless consistency makes your test results far more reliable and trustworthy.
By offloading the repetitive grunt work to machines, you empower your talented QA professionals to focus on what they do best: exploratory testing, usability analysis, and creative problem-solving. It's a win for your product and a win for your team's morale.
Navigating Common GUI Automation Challenges
While the benefits of GUI automation are huge, the path to getting there isn't always a straight line. Teams often hit a few common hurdles that can kill momentum and lead to a lot of frustration. Knowing what these challenges are ahead of time is the first step to building a test strategy that can actually withstand the pressures of modern development.
The good news? These problems are all solvable. With the right mindset and a few solid practices, you can turn these roadblocks into learning experiences that make your entire quality process stronger. Let's break down the most common obstacles and talk about how to get around them.
The Problem of Brittle Tests
One of the first complaints you’ll hear about automated GUI tests is that they’re "brittle." What this means is that a tiny, seemingly harmless change to the UI can shatter an entire test script. Picture this: a developer changes a button's ID or tweaks a CSS class name. Suddenly, your perfectly good test fails—not because the feature is broken, but because the script can no longer find the element it was told to look for.
This brittleness kicks off a vicious cycle. Instead of writing new tests to cover more ground, your team gets bogged down fixing old ones over and over again. This constant maintenance erodes the ROI of automation and can make the whole effort feel like a waste of time. If you let it go on for too long, your team might lose faith in the test suite entirely.
To fight this, you have to build resilience into your test design from day one.
The core challenge isn't automation itself, but how you implement it. Brittle tests are usually a symptom of a test design that's too tightly coupled to the UI's code, rather than its intended behavior.
The key is to focus on smart test structures and robust ways of finding elements on the page. That's how you create a suite that lasts.
Building Resilience with Stable Locators
The secret to durable tests is all about how your scripts identify elements in the UI. Instead of latching onto fragile properties that change all the time, you need to prioritize more stable attributes. This one shift in strategy can slash your test maintenance time.
Here are a few best practices for picking your locators:
- Prioritize Unique IDs: A unique
data-testidoridis your best bet. Work with your developers to get these added specifically for testing purposes. - Use Descriptive Attributes: Look for things like
name,aria-label, or other accessibility markers that describe what an element does. These change far less often than stylistic classes. - Avoid Positional Locators: Relying on an element's position (e.g., "the third button in the list") is a recipe for disaster. Any layout change will break your test.
- Be Cautious with CSS Classes: Developers change CSS classes for styling all the time, which makes them a risky and unstable choice for test automation.
By choosing locators based on function instead of appearance, your tests become way more resistant to the constant churn of UI development.
Managing Dynamic Content and Wait Times
Modern web apps are anything but static. Content often loads asynchronously, elements pop up after a delay, and animations can affect when a button is actually clickable. A test script that plows ahead too quickly will fail simply because it tried to interact with an element that wasn't there yet. This is what leads to flaky tests—the ones that pass sometimes and fail others for no obvious reason.
Flakiness is poison for a test suite. If the team can't trust the results, they'll just start ignoring them.
The solution is to build intelligent "waits" into your scripts. Forget about fixed delays like "wait 5 seconds," which are both inefficient and unreliable. Instead, use dynamic waits. This means you program the script to wait for a specific condition—like an element becoming visible or clickable—before it moves on. This simple change makes your tests both faster and more dependable because they adapt to how the application is actually behaving in real-time.
Choosing the Right Automated GUI Testing Tool
Picking the right tool for your automated GUI tests is one of those big decisions that will echo through your entire quality assurance strategy. The market is absolutely flooded with options, and every single one of them promises to be your silver bullet. But here's the reality: there's no such thing as the single "best" tool. There's only the tool that's best for your team, your project, and your unique goals.
The trick is to look past the shiny feature lists and get real about your development environment. A super-powerful tool that your team can't figure out is far worse than a simpler one they can actually master. You're looking for that sweet spot where technical power, team skills, and budget all meet. Get this right, and you've set your automation efforts up for long-term success.
This infographic breaks down the core differences between manual and automated testing, really driving home why this tool decision is so important for upping your game.
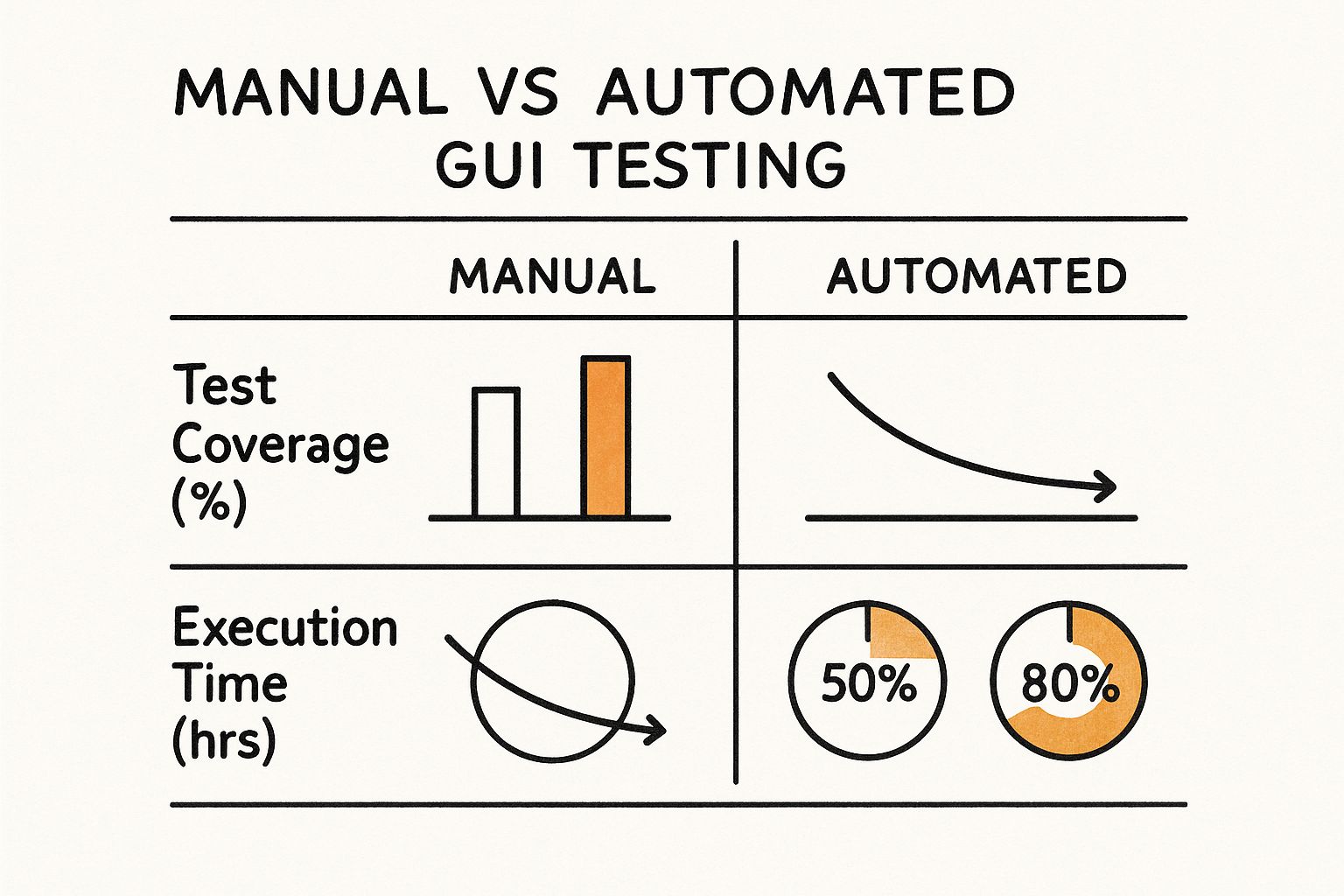
As you can see, automation blows manual testing out of the water in coverage, speed, and finding defects early. That makes your tool choice a high-stakes decision.
Code-Based vs. Codeless Solutions
Your first big fork in the road is choosing between a code-based tool and a codeless (or low-code) one. This really comes down to who’s on your team and how you want to manage your test scripts.
- Code-Based Tools: Think frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright. These demand real programming chops. They give you ultimate flexibility and power, making them a perfect fit for teams with strong developers who are comfortable writing tests in languages like JavaScript or Python.
- Codeless Tools: Platforms like ACCELQ or Katalon Studio are built for teams with a mix of technical skills. They use visual interfaces, recorders, and drag-and-drop features so QA specialists, and even business analysts, can build robust tests without writing a line of code.
There's no wrong answer here. A team full of senior devs might feel boxed in by a codeless tool, while a QA-focused team could get bogged down by the steep learning curve of a programming-heavy framework.
Open-Source vs. Commercial Tools
Next up, you have to weigh the pros and cons of open-source versus commercial products. This isn't just about money; it’s about support, built-in features, and the ecosystem you're buying into.
Open-Source Tools (e.g., Selenium, Playwright):
- The Good: They’re free, incredibly flexible, and backed by huge, active communities. If you have a problem, chances are someone has already solved it and posted the answer online.
- The Catch: You're on your own for setup and configuration. Support comes from community forums, so there’s no dedicated helpdesk to call when you're stuck.
Commercial Tools (e.g., TestComplete, Tricentis Tosca):
- The Good: These are often polished, all-in-one solutions. You get dedicated customer support, professional documentation, and enterprise-grade features like slick reporting and easy integrations.
- The Catch: They come with license fees that can add up quickly. You also risk getting locked into a single vendor's ecosystem.
Ultimately, you have to balance your budget against your need for hand-holding and out-of-the-box functionality. A lean startup will likely gravitate toward open-source, while a large enterprise might prefer the security and support that comes with a commercial license.
To help you get a clearer picture, here's a quick rundown of some popular tools and where they fit.
Popular GUI Automation Tool Comparison
This table gives you a high-level look at some of the leading tools out there, helping you map their strengths to your team's needs.
| Tool | Primary Use Case | Key Feature | Skill Level Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selenium | Cross-browser web automation | Language flexibility (Java, Python, C#, etc.) | High (Coding) |
| Cypress | Modern web app testing (React, Vue, etc.) | Real-time reloads, interactive test runner | Medium (JavaScript) |
| Playwright | End-to-end web & mobile web testing | Auto-waits, cross-browser consistency (Chromium, Firefox, WebKit) | Medium (JavaScript/TypeScript) |
| Katalon Studio | All-in-one testing (Web, API, Mobile) | Low-code interface with optional scripting | Low to Medium |
| TestComplete | Enterprise desktop, web, & mobile testing | AI-powered object recognition, record & replay | Low to High |
Choosing the right tool is about finding the one that feels like a natural extension of your team, not an obstacle to overcome.
Key Factors for Your Decision Framework
Now that you know the landscape, you can start building a framework for making your final call. The UI test automation software market is booming—it was valued at USD 1.5 billion and is expected to hit USD 4.2 billion by 2033, which shows just how vital this has become. You can dig into more of the numbers on the UI test automation software market trends on verifiedmarketreports.com.
Here are the critical questions your team needs to answer:
- What’s our team’s skill set? Are we devs who live in code, or do we need something that empowers our manual testers to automate?
- What’s our application's tech stack? Make sure the tool you pick plays nicely with your specific frameworks (like React or Angular) and platforms (web, mobile, desktop).
- What’s our real budget? Don't just look at the license cost. Factor in the time and money you'll spend on training, setup, and maintenance.
- How critical is CI/CD integration? Your tool has to plug right into your pipeline (Jenkins, GitHub Actions, etc.) to give you that fast, continuous feedback loop.
- Will this scale with us? Think about the future. Does the tool support running tests in parallel? What about cross-browser testing? Choose something that won’t hold you back in a year.
By working through these questions, you can cut through the marketing noise and find a tool that will genuinely help your team build and maintain a top-notch suite of automated GUI tests.
Best Practices for Building Maintainable GUI Tests
Anyone can write a script that clicks a few buttons. That’s the easy part. The real challenge is building a suite of automated GUI tests that actually stands the test of time. Your goal isn't just to write tests; it's to create a robust, low-maintenance asset that consistently delivers value.
Without a solid strategy, it’s easy to end up with a tangled mess of brittle scripts. You know the kind—they break with every minor UI change and cost more time to fix than they save. This is where smart design patterns and a few proven best practices come into play. By thinking structurally from the start, you can build a test framework that is resilient, easy to read, and simple to update.
Embrace the Page Object Model
One of the most powerful strategies you can adopt is the Page Object Model (POM). Think of POM as creating a map of your application's UI inside your test code. Instead of scattering element locators and interaction logic all over your test scripts, you group them into dedicated "page objects."
Each page object represents a specific screen or even a major component, like a login form or a navigation bar. This object holds all the locators for the elements on that page and the methods to interact with them (like enterUsername() or clickLoginButton()).
This approach pays off big time:
- Reduced Code Duplication: If a UI element changes, you update its locator in just one place: the page object. No more hunting through dozens of different test scripts.
- Improved Readability: Your tests start to read like a series of high-level user actions (
loginPage.loginAsUser("test", "pass")) instead of a confusing sequence of clicks and waits. - Enhanced Reusability: Page objects can be used across many different tests, making your entire suite more efficient and much easier to scale.
Write Small, Independent Tests
It’s tempting to create massive, end-to-end tests that validate an entire user workflow in one go. While these have their place, relying on them too heavily is a recipe for headaches. When one of these monolithic tests fails, figuring out the exact cause of the problem can be a nightmare.
A much better approach is to break your tests down into small, independent, and focused units. Each test should have a single, clear purpose. For example, instead of one giant "purchase a product" test, you could have separate tests for:
- Searching for a product.
- Adding a product to the cart.
- Proceeding to the checkout page.
- Entering payment details.
This modular structure makes your tests far easier to write, debug, and maintain. When a test fails, you know precisely which piece of functionality is broken. For a deeper look into this and other core principles, our guide on automated testing best practices is a great resource.
Master Smart Waits, Not Hard Sleeps
Modern web apps are dynamic. Content loads asynchronously, which means elements don't always appear on the page instantly. A test script that plows ahead too quickly will fail simply because it tried to click something that wasn't there yet. This leads to "flaky" tests—the frustrating kind that pass sometimes and fail others for no obvious reason.
The worst way to handle this is with fixed delays, or "hard sleeps" (e.g., sleep(5)). This forces your test to just sit there for a fixed time, making it slow and unreliable. There's a much better way: smart waits.Smart waits tell the test script to pause until a specific condition is met—like an element becoming visible or clickable. This makes your tests both faster and infinitely more reliable because they adapt to your application's real-time performance instead of guessing.
Integrating GUI Tests Into Your CI/CD Pipeline
Let's be honest, the real magic of automated GUI tests doesn't happen when you're manually clicking "run." It's when they disappear into the background, becoming a seamless, invisible part of your daily development workflow. By plugging them into a Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipeline, you transform them from an occasional spot-check into a relentless quality guardian.
When you do this, testing is no longer an afterthought. It becomes an active quality gate that fires off with every single code change. This gives developers feedback when it matters most—right after they’ve pushed their code.
From Manual Checks to Automated Quality Gates
A CI/CD pipeline is all about automating the build, test, and deployment process. When you slot your automated GUI tests into this pipeline, you create an incredibly powerful and immediate feedback loop. Tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions can be set up to trigger your entire GUI test suite every time a developer commits new code or opens a pull request.
Think of it as an automated checkpoint. If a test fails, the pipeline halts, blocking the faulty code from moving any further. This instant feedback helps developers catch and fix regressions in minutes, not days or weeks down the line. For a great primer on the core ideas, understanding Continuous Integration is a must-read for any modern development team.
This automated approach ensures quality isn't just a vague goal but a baked-in, non-negotiable part of your process. It fundamentally shifts the team's mindset from "we'll test it later" to "let's build it right the first time."
"When GUI tests are seamlessly integrated into your CI/CD pipelines, they run automatically with every code commit. This enables early bug detection, faster feedback loops, and significantly improves the stability of each release."
By embedding these tests directly into the development cycle, you guarantee that every single merge makes your application more stable, not less.
Tools like Mergify are perfect for managing this flow. They create an intelligent merge queue that ensures only validated, passing code ever makes it into your main branch. It’s a clear picture of how automation can bring a sense of calm and order to an otherwise chaotic development process.
The Key Benefits of Pipeline Integration
Weaving your GUI test suite into your CI/CD process pays off in some huge ways, directly boosting your team’s speed and your product's quality. This is exactly what applying modern continuous integration best practices is all about.
Here’s what you stand to gain:
- Instant Feedback: Developers find out immediately if their changes broke something in the user interface. No more painful context-switching to fix bugs found days later.
- Reduced Risk: You catch UI regressions early, stopping them long before they can ever reach production. This saves your users from a frustrating experience and protects your brand's reputation.
- Increased Confidence: When the whole team knows a comprehensive suite of GUI tests has already passed, they can push out new features with way more speed and confidence.
- Improved Collaboration: A shared, automated pipeline creates a culture of collective ownership over quality. It's no longer "QA's job"—it's everyone's responsibility.
Ultimately, pipeline integration turns your automated GUI tests from a simple safety net into a powerful engine for accelerating development while ensuring rock-solid quality. It's the final piece of the puzzle that makes automation a true strategic advantage for your team.
Got Questions About Automated GUI Tests?
As teams start to weave GUI automation into their workflow, a few practical questions always pop up. It's totally normal. Getting these sorted out early ensures everyone's on the same page and you're building your strategy on solid ground.
Here are some of the most common questions I hear, along with some straight-up answers.
Which Test Cases Should I Automate First?
This is a big one. My advice? Go for the biggest and fastest return on your effort. You want to automate the tests that are both high-value and mind-numbingly repetitive.
Good places to start include:
- Business-Critical Workflows: Think about the absolute must-work parts of your app. User login, registration, password recovery, and the checkout process are perfect candidates. If these break, you're in trouble.
- Smoke Tests: These are your quick, first-line-of-defense checks. They cover the most fundamental features to make sure the build isn't completely broken. Automating these is a huge win for stability.
- Data-Driven Tests: Got a feature that needs to be tested with a dozen different user inputs or account types? That's a prime target. Let the machine do the grunt work.
Can Automated GUI Tests Replace Manual Testing?
Nope. And they shouldn't. Think of them as partners in a solid quality strategy, not rivals.
Automated GUI tests are absolute rockstars at repetitive, predictable tasks like regression testing. They make sure existing features don’t break when you add new code. They're fast, precise, and never get tired or bored.
But you'll always need manual testing for anything that requires a human touch. This is where exploratory testing, usability assessments, and checking complex visual designs come in. Automation is the powerful assistant that frees up your human testers to focus on what they do best: thinking creatively and critically.
Think of automation as the tireless security guard who checks that every window and door is locked, while the manual tester is the architect who evaluates the building's flow, feel, and overall user experience.
What’s the Difference Between GUI and End-to-End Testing?
They're definitely related, but they don't cover the same ground. It really comes down to scope.
GUI testing is laser-focused on the user interface itself. It's all about verifying that buttons, menus, and forms look right and work as expected. Does the button click? Does the dropdown menu open?
End-to-end (E2E) testing is the big picture. It validates an entire user journey from the moment they start to the moment they finish. This includes the GUI, but it also dives deeper to check interactions with the backend, databases, and any third-party APIs. It's about confirming the entire system works together in harmony.
Accelerate your development and ensure rock-solid code with Mergify. Our platform automates your merge queue, protects your codebase, and provides deep CI insights to eliminate bottlenecks. See how Mergify can streamline your entire workflow at https://mergify.com.