Automating GUI Testing in Your CI/CD Workflow
So, what do we actually mean when we talk about automating GUI testing? It's the practice of using specialized software tools to run tests on a graphical user interface, checking both its functionality and appearance without anyone having to manually click through screens. This isn't just a "nice to have" for modern dev teams; it's essential. It dramatically speeds up the testing process, boosts accuracy, and allows you to run frequent, repeatable checks on your UI. By automating these tests, teams can spot bugs much earlier in the cycle and, ultimately, ship higher-quality software faster.
Why Automating GUI Testing Is a Competitive Edge
Let's be honest—in today's development world, sticking to manual-only GUI testing is like tying one hand behind your back. It might feel like enough for a small, simple project, but it quickly becomes a massive bottleneck in any modern Agile or DevOps workflow. Manual checks are just plain slow, and that creates delayed feedback loops that kill your team's momentum.
And then there's the human element. Manual testing is susceptible to human error. A tester might miss a subtle visual regression that broke on a different screen resolution, or they could forget one crucial step in a complex user journey. These little inconsistencies can easily let bugs slip through to production, damaging the user experience and your company’s reputation.
The Scaling Problem with Manual Checks
The limitations of manual testing become glaringly obvious as your application gets bigger and more complex. Imagine your team just shipped a new feature that touches ten different user flows. A manual tester would have to meticulously re-test every single one of those flows. We're talking hours, maybe even days, of repetitive work. That approach just doesn't scale.
This is precisely where automating your GUI tests moves from being an efficiency boost to a strategic necessity. Automated scripts can blaze through hundreds of regression tests in minutes, giving your developers immediate feedback on every single commit.
This frees up your talented QA professionals to focus on high-value work that actually requires human intuition and creativity, such as:
- Exploratory Testing: Actively trying to break the application in unexpected ways to uncover hidden bugs.
- Usability Testing: Gauging how intuitive and user-friendly the application actually feels to a real person.
- Edge Case Analysis: Digging into complex scenarios and tricky user paths that automated scripts might not cover.
By shifting from repetitive manual checks to a robust automation strategy, you transform your QA process from a reactive bottleneck into a proactive quality gate. It’s a move that directly supports faster innovation and a stronger market position.
The growing emphasis on user experience is driving serious investment in this space. The GUI Testing Tool market was valued at around USD 2.5 billion and is on track to hit USD 6 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 12.5%. This trend makes it clear how critical automation is for delivering the seamless digital products users expect. For a deeper look at what's driving this growth, check out the analysis on Verified Market Reports.
Choosing The Right GUI Automation Framework
Picking a framework for your automated GUI tests is a huge decision. It's one of those foundational choices that will ripple through everything, from how fast your team can write scripts to how much of a headache maintenance becomes down the line. It's easy to get analysis paralysis with all the options out there, but you can cut through the noise by focusing on your team's reality, not just a flashy feature list.
For instance, if your team already lives and breathes Python, picking a framework that uses it will dramatically lower the barrier to entry. Everyone can get up to speed faster. On the flip side, grabbing the hot new tool without considering your project's tech stack is a recipe for friction. A framework built for a slick, modern single-page app might be total overkill—or just a terrible fit—for your legacy desktop software.
The real goal here is to find a tool that slots neatly into your current workflow, not one that forces you to tear everything down and start over.
Key Decision Factors To Consider
Before you even start looking at specific tools, run through this mental checklist. It'll help you evaluate potential frameworks against what actually matters for your team.
- Language and Skill Alignment: Does the framework use a language your developers already know inside and out, like JavaScript, Python, or Java? Sticking with existing expertise is the single fastest way to get your automation effort off the ground.
- Ecosystem and Community Support: A vibrant community is a massive asset. It means better documentation, more third-party plugins, and a huge pool of shared knowledge you can tap into when you get stuck. Big open-source players like Selenium and Cypress have enormous communities, which is a great safety net.
- Integration Capabilities: How easily will this tool plug into your CI/CD pipeline? You need something that plays nice with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or whatever you're using. The whole point is to make these GUI tests a fully automated quality gate, so seamless integration is non-negotiable.
- Target Application Technology: What are you actually testing? Is it a web app built with React? A native iOS app? A clunky old desktop client? Your framework must be compatible with the tech you're targeting. Playwright, for example, is brilliant for modern web apps, but you'd need something else entirely for a different environment.
This is the kind of real-world impact you can expect when you get your automation strategy right.
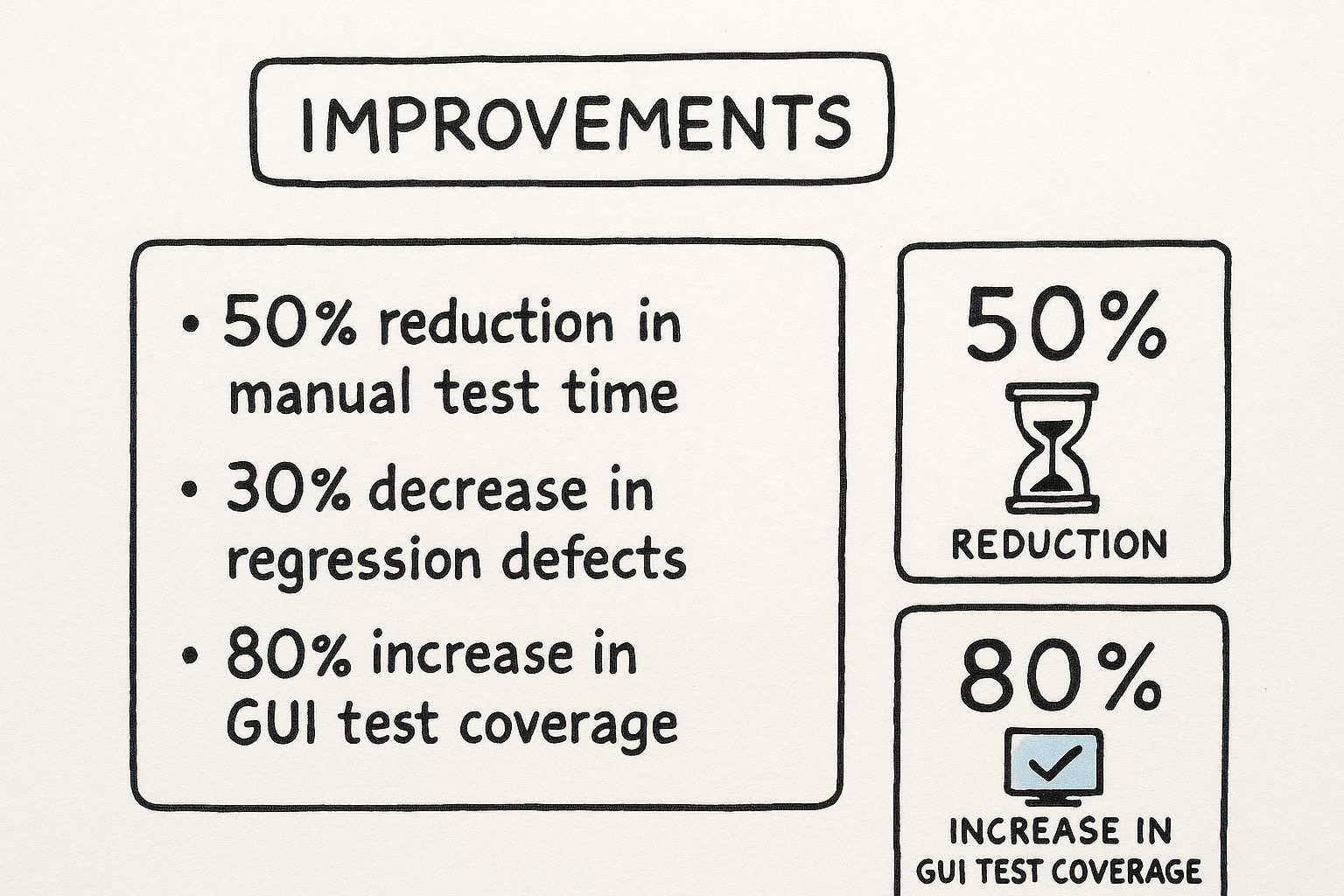
As you can see, solid automation directly leads to fewer bugs escaping into production and a huge boost in test coverage.
Comparing Popular GUI Automation Frameworks
To give you a better sense of the landscape, let's look at a few of the heavy hitters side-by-side. This table isn't about crowning a single "best" tool, but helping you find the best fit for the job at hand.
| Framework | Primary Language | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selenium | Java, Python, C#, etc. | Cross-browser testing at a massive scale for complex web applications. | Unmatched flexibility and language support; it adapts to almost any environment. |
| Cypress | JavaScript / TypeScript | Modern web applications, especially those built with JavaScript frameworks. | A fantastic developer experience with real-time reloads and dead-simple debugging. |
| Playwright | JavaScript / TypeScript | End-to-end testing of modern web apps needing multi-browser coverage. | Blazing fast, reliable execution and powerful features like network interception. |
| TestComplete | VBScript, JavaScript | Enterprise-level testing of desktop, web, and mobile applications. | An all-in-one commercial solution with incredibly robust object recognition. |
At the end of the day, picking the right framework comes down to one simple truth: the best tool is the one your team will actually use.
A technically superior framework that sits on a shelf collecting digital dust is worthless. A "good enough" tool that's deeply embedded in your team's daily habits, on the other hand, is invaluable. Always prioritize usability and team fit above all else.
Writing Resilient and Maintainable Test Scripts
The real test of a GUI automation strategy isn't getting a script to pass once. It's about building tests that don't shatter the moment a developer tweaks a CSS class or renames a button.
Brittle tests are the number one reason automation efforts collapse. Teams get buried in a soul-crushing cycle of script maintenance, fixing things that were never really broken. The whole point is to create a test suite that can roll with the punches as your UI evolves, freeing up your team to build new tests, not just patch up old ones.
A few smart practices can make all the difference.
Decouple UI Elements with the Page Object Model
One of the most powerful strategies I've seen for boosting maintainability is the Page Object Model (POM). It's a design pattern that completely changes the game by separating what you’re testing (your test logic) from how you find elements on the page.
Instead of hardcoding CSS selectors or XPath locators right into your test steps, you create a dedicated class for each page or major component of your app. This class acts as a single source of truth, holding all the locators and methods for interacting with that specific part of the UI.
- Your Test Script: Calls a clean, readable method like
loginPage.enterUsername('testuser'). - Your Page Object: Contains the messy implementation details, like
driver.findElement(By.id('user-name-field')).sendKeys('testuser').
Now, when a developer inevitably changes the ID of the username field, you only update it in one place: the LoginPage object. You're not digging through dozens of scripts to fix the same broken locator. It's a simple shift that makes your test suite infinitely easier to manage and debug.
By abstracting the UI implementation details away, the Page Object Model forces your tests to focus on actual user behavior. This not only makes them more robust but also far more readable for everyone on the team, from QA to product managers.
Implement Smart Waits, Not Static Sleeps
Modern web apps are fundamentally asynchronous. Content loads dynamically, and elements pop into existence when they’re ready—not on a fixed schedule. A classic rookie mistake is scattering fixed delays, or "sleeps," throughout the code to wait for things to appear. This is a horribly unreliable approach. Your tests will either fail when the app is slow or waste precious time when it's fast.
The professional approach is to use explicit waits. You tell your automation framework to wait for a specific condition to be met before moving on—like an element becoming visible or clickable. This small change makes your tests faster and significantly more reliable because they adapt to the application's real-time performance. It's also a crucial first step in tackling intermittent failures and is a core part of any good strategy for flaky test detection.
Writing Stable Selectors
The final piece of this puzzle is choosing the right locators in the first place. Relying on those long, complex, auto-generated XPath or CSS selectors is just asking for flaky tests.
Instead, prioritize selectors that are both stable and descriptive. The absolute best practice? Work with your developers to add unique, test-specific attributes to key elements, like data-testid. These custom attributes are insulated from UI redesigns, making them the most reliable hooks you can get for your automated tests.
As more teams embrace automation, the benefits become impossible to ignore. Industry data shows 46% of software teams have now automated more than half of their testing workload. As you build out your own robust scripts, it's always a good idea to cross-reference a comprehensive mobile app testing checklist to ensure you're not missing any critical user scenarios.
Integrating Automated Tests Into Your CI/CD Pipeline
This is the moment where all the effort you put into automating GUI testing really starts to pay off. When you embed those slick test scripts directly into your CI/CD pipeline, you're not just running tests anymore. You're building a powerful, automated quality gate.
This is a critical step. It ensures no new code gets merged until it proves it won't break the user experience.
The concept is simple but incredibly effective. Instead of running tests manually or on some ad-hoc schedule, they become a core part of your daily development workflow. Every time a developer opens a pull request, the pipeline automatically kicks off, running your entire GUI test suite against the proposed changes.
Think of it as the ultimate safety net.
Configuring Your Pipeline Triggers
First things first, you need to set up the trigger that kicks off the tests. In most modern CI/CD tools like GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Jenkins, this is pretty straightforward. You'll just need to configure a workflow file—usually a .yml file—to listen for specific events.
A common and highly effective strategy is to trigger the GUI test suite on every pull_request event. This means as soon as a PR is up for review, the tests are already running.
This gives developers immediate feedback directly within the pull request. They can see if their changes caused a regression before a human reviewer even lays eyes on the code. It’s a proactive approach that catches bugs at the earliest possible moment.
A GitHub Actions workflow, for instance, might look something like this:
name: GUI Tests
on:
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
run-gui-tests:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Setup Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: '18'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm install
- name: Run Playwright tests
run: npx playwright test
This simple configuration ensures that every PR targeting the main branch is automatically validated. For a deeper dive into setting this up with a specific framework, our guide on https://articles.mergify.com/automated-playwright-testing/ offers a detailed walkthrough.
Managing Environments and Parallel Execution
One of the biggest hurdles in CI is managing test environments and keeping the pipeline from turning into a slog. You absolutely need a clean, consistent environment for every test run to avoid flaky results and false negatives. Containerization tools like Docker are perfect for this, letting you spin up a pristine application and database for each pipeline execution.
But here’s the catch: a comprehensive GUI test suite can be slow. Waiting 30 minutes for feedback on a pull request is a non-starter for fast-moving teams. The solution? Parallelization.
By running your tests in parallel across multiple virtual machines or containers, you can slash execution time from minutes to moments. Most modern test runners and CI platforms offer built-in support for sharding your test suite, drastically shortening the feedback loop.
This isn’t just about speed; it’s about protecting developer velocity. When tests are fast, they remain a helpful part of the process instead of becoming a frustrating bottleneck.
For a truly comprehensive quality approach, you can also integrate performance tests. For applications built on frameworks like Ruby on Rails, you can explore specialized options like Ruby on Rails Performance Services for deeper insights.
Finally, make sure your pipeline provides instant, clear notifications. When a test fails, the right people need to know immediately. Configure your CI tool to post results directly to the pull request and send alerts via Slack or email. Clear, actionable feedback is what makes your automated quality gate a true asset to your team.
Right, so you’ve got your GUI tests running in the pipeline. That’s a huge first step. But the real magic happens when you start making the whole process smarter and more efficient.
This is where AI is starting to feel less like a buzzword and more like a genuinely useful tool for GUI testing. It's not some far-off concept anymore; it's a practical way to build test suites that are more resilient and, frankly, less of a pain to maintain.
We're seeing this shift happen across the board. About 42% of large companies are already using AI in some form, and that includes AI-driven testing. The teams who get on board with this are seeing big drops in their testing cycle times. You can dig into more of the numbers over at TestGrid's software testing statistics if you're curious.
The Rise of AI in Test Automation
AI is tackling some of the most common headaches that come with GUI automation. The biggest win, in my opinion, is self-healing tests.
Think about it: how many times has a test failed just because a developer changed a button's ID? It's infuriating. AI-powered tools can get around this by intelligently identifying the element based on other attributes, then automatically updating the locator. This one feature alone can slash the tedious, mind-numbing maintenance that kills so many automation projects.
Another area where AI is a game-changer is in visual regression testing. These tools are getting incredibly sophisticated. They can:
- Spot visual bugs intelligently, understanding the page layout and ignoring tiny rendering quirks that would normally trigger false alarms.
- Catch unexpected UI changes that a functional test would completely miss, keeping your application looking consistent.
- Speed up visual validation by only showing you the meaningful differences that need a human eye, saving hours of review time.
These aren't just minor improvements; they make your entire test suite more robust and far less brittle. We’ve written before about how AI in automated testing is helping create tests you can actually trust.
Connecting Advanced Tests with Smart Merging
Now, having smarter tests is great, but it’s only half the equation. You need a workflow that can automatically act on their results. This is exactly where a tool like Mergify slots in. By setting up an automated merge queue, you essentially create a non-negotiable quality gate for your main branch.
A merge queue ensures that no pull request is merged until all required checks, including your advanced GUI tests, have passed on the very latest version of the target branch. It effectively eliminates merge conflicts and stops broken code in its tracks.
This setup creates a powerful, hands-off feedback loop. Your developers get clear, immediate signals on their code's quality without anyone having to manually check or trigger anything.
If the AI-powered visual tests spot a regression, the PR is automatically blocked. If the self-healing functional tests pass, the code is safely merged into the main branch. This frees up your team to focus on what they do best—building features—with the confidence that an intelligent, automated system is protecting the codebase.
Gotchas and Questions in GUI Test Automation
Even with the best-laid plans, you're bound to run into a few tricky spots when you start automating GUI tests. Let's walk through some of the most common questions and roadblocks teams hit, so you can navigate them like a pro.
How Do You Handle Dynamic Elements?
Ah, dynamic elements. They're one of the biggest headaches in GUI automation. You know the ones—those buttons or fields where the ID or attributes seem to change every single time the page loads. If you rely on those fragile, auto-generated selectors, you're just signing up for a future of flaky tests.
The trick is to build resilient locators. Forget about that volatile ID. Instead, you need to get a bit more creative and stable with your strategy:
- Can you find the element based on its text? If the button always says "Submit," use that. It's far less likely to change than some random ID.
- Look at what's around it. Use relative selectors like XPath or CSS to anchor the dynamic element to a stable neighbor. Think "the input field to the right of the 'First Name' label."
- Better yet, collaborate with your developers. Ask them to add dedicated test attributes like
data-testidto the code. These are put there specifically for automation and almost never change, making your tests rock-solid.
What's the Real Difference Between End-to-End and GUI Testing?
It's easy to get these two mixed up, and you'll often hear people use the terms interchangeably. But they're really testing different things.
GUI testing is all about the user interface itself. It’s hyper-focused on the visual and interactive parts. You’re answering questions like, "Does this button look right?" or "Can I type text into this form field?" It’s a very specific validation of what the user sees and clicks.
End-to-end (E2E) testing, on the other hand, is the whole shebang. It simulates a complete user journey from start to finish. That journey includes clicking around the GUI, but it also goes deeper to verify that all the connected backend services, databases, and APIs are playing nicely together.
Think of it this way: all E2E tests involve some form of GUI testing, but not all GUI tests are full-blown E2E tests.
A word of advice: trying to hit 100% GUI test automation is a trap. It's often a waste of resources for diminishing returns. The smartest teams focus on automating the repetitive, high-risk regression tests. Save your manual testing efforts for exploratory and usability checks where a human's intuition is still king.
Ready to build a powerful, automated quality gate that stops bad code in its tracks? With Mergify, you can set up a smart merge queue that only merges pull requests after all your GUI tests have passed. No more broken code making it to your main branch. Learn more and see how Mergify can optimize your workflow.