What is Deployment Automation? Boost Your Software Delivery
Deployment automation is all about taking the human element—and human error—out of pushing code live. It’s the practice of using tools to handle all the tedious, manual steps involved in a software release. This creates a reliable and repeatable process that moves new code from a developer’s machine to a production environment without anyone having to hold their breath.
What used to be stressful, late-night release parties can now become predictable, routine, and frankly, a little boring. And in the world of software deployment, boring is a very good thing.
From Manual Chaos to Automated Order
Think of a high-tech kitchen where ingredients are automatically prepped, cooked, and plated perfectly every time, with no chef frantically running around. That’s a great way to picture what deployment automation does for your code.
Instead of a developer manually copying files, tweaking server configurations, and restarting services—a process just begging for a typo to bring everything down—automation builds a dependable "assembly line" for your code. This system doesn't just reduce the chance of human error; it eliminates it by ensuring every single deployment is consistent.
This shift is a cornerstone of modern software development. The goal is to make deployments so routine they become non-events, empowering teams to release updates frequently and with total confidence.
The Problem with Manual Deployments
We’ve all been there. Manual deployments are often stressful, all-hands-on-deck affairs. A single forgotten step or a slightly off configuration can crash an entire application, leading to downtime, frustrated users, and a weekend spent troubleshooting.
- High Risk of Human Error: It’s so easy to make a simple mistake, like deploying the wrong branch or missing a single configuration setting. The consequences can be massive.
- Inconsistent Environments: When servers are configured by hand, tiny differences between staging and production can cause deployments to fail in the most unexpected ways. What worked perfectly a minute ago is now broken in production.
- Slow Release Cycles: The sheer time and effort required for manual releases often mean updates get bundled into huge, infrequent deployments. This delays new features and critical bug fixes from reaching your users.
To better understand the contrast, let's look at a side-by-side comparison.
Manual Deployment vs Automated Deployment
| Aspect | Manual Deployment | Automated Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Ad-hoc, relies on checklists and human memory. | Standardized, codified, and executed by tools. |
| Speed | Slow, often takes hours or days. | Fast, can be completed in minutes. |
| Risk of Error | High, prone to human mistakes. | Minimal, errors are caught early by the system. |
| Consistency | Low, environments can drift and differ. | High, every deployment is identical. |
| Developer Focus | On the mechanics of deploying. | On building features and writing code. |
| Scalability | Poor, becomes unmanageable with more services. | Excellent, scales effortlessly with the application. |
This table makes it clear: automation isn't just about convenience; it’s a fundamental change in how software is delivered.
The Power of an Automated Assembly Line
Deployment automation tackles these challenges by creating a structured, repeatable workflow. By turning the entire process into code, it guarantees that every deployment follows the exact same steps, from the first build and test to the final release. This systematic approach isn't just a technical upgrade; it's a powerful business advantage.
By automating the release process, teams can shift their focus from firefighting deployment issues to building valuable features that drive the business forward. It transforms software delivery from a bottleneck into an accelerator for innovation.
The industry has taken notice. The deployment automation market, currently valued at around USD 1.7 billion, is on a steep upward trajectory. Projections show it’s expected to nearly triple, hitting an estimated USD 5.5 billion by 2033.
This incredible growth underscores just how critical automated systems have become for modern IT. Of course, as automation becomes a central part of a CI/CD pipeline, security is paramount. It’s crucial to understand and implement key CI/CD security best practices to protect your newly automated workflows from new threats.
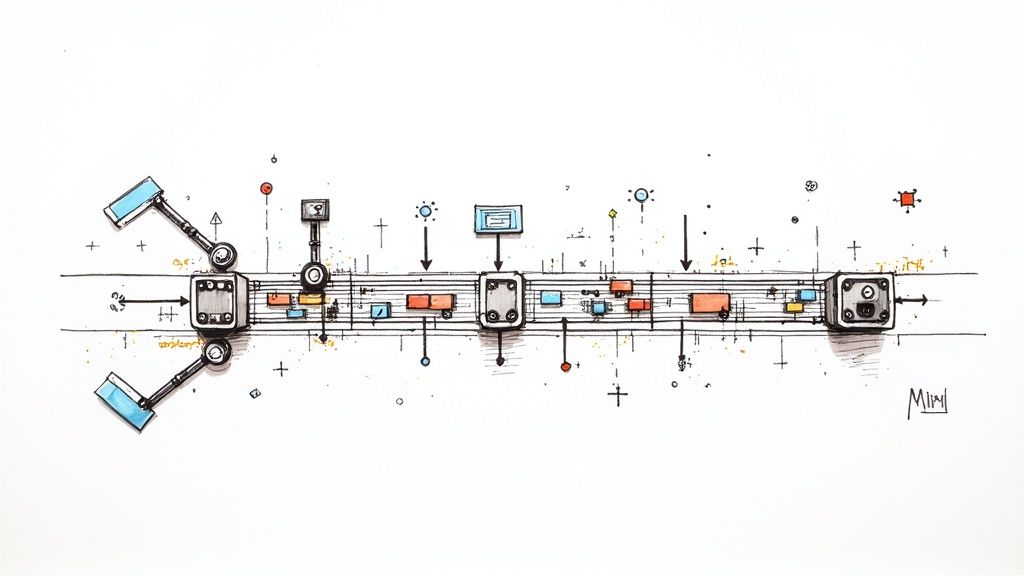
How a Deployment Automation Pipeline Actually Works
To really get what deployment automation is, you have to look under the hood at the pipeline that makes it all happen. Picture it as a sophisticated, automated assembly line for your software. Every stage has a specific job, making sure the code is built, tested, and delivered safely and efficiently—all without a human touching it.
The whole thing kicks off the second a developer commits new code to a version control system like Git. That single action is the trigger, telling the system that a new batch of code is ready to go down the line.
From Code Commit to Ready-to-Ship Artifact
Once the code is committed, a build server—think tools like Jenkins or GitLab CI—jumps into action. This server is like the first quality control inspector on our assembly line. It pulls the latest code from the repository and starts the build process, compiling it into an executable application.
Right after a successful build, a whole suite of automated tests runs. This usually includes:
- Unit Tests: These check that individual pieces of the code work correctly on their own.
- Integration Tests: These make sure that different parts of the app play nicely together.
If any test fails, the pipeline slams on the brakes. The developer gets an immediate notification, and the flawed build goes no further. But if everything passes, the pipeline packages up the compiled code and all its dependencies into a single, versioned bundle called an artifact. This is your self-contained, ready-to-deploy unit.
The whole point of a deployment pipeline is to create a consistent, repeatable artifact. This guarantees that the exact same code that passed all the tests is what gets deployed everywhere, killing the classic "it worked on my machine" problem for good.
This flow is all about moving code from a developer's commit through the build, test, and deployment stages in a controlled way.
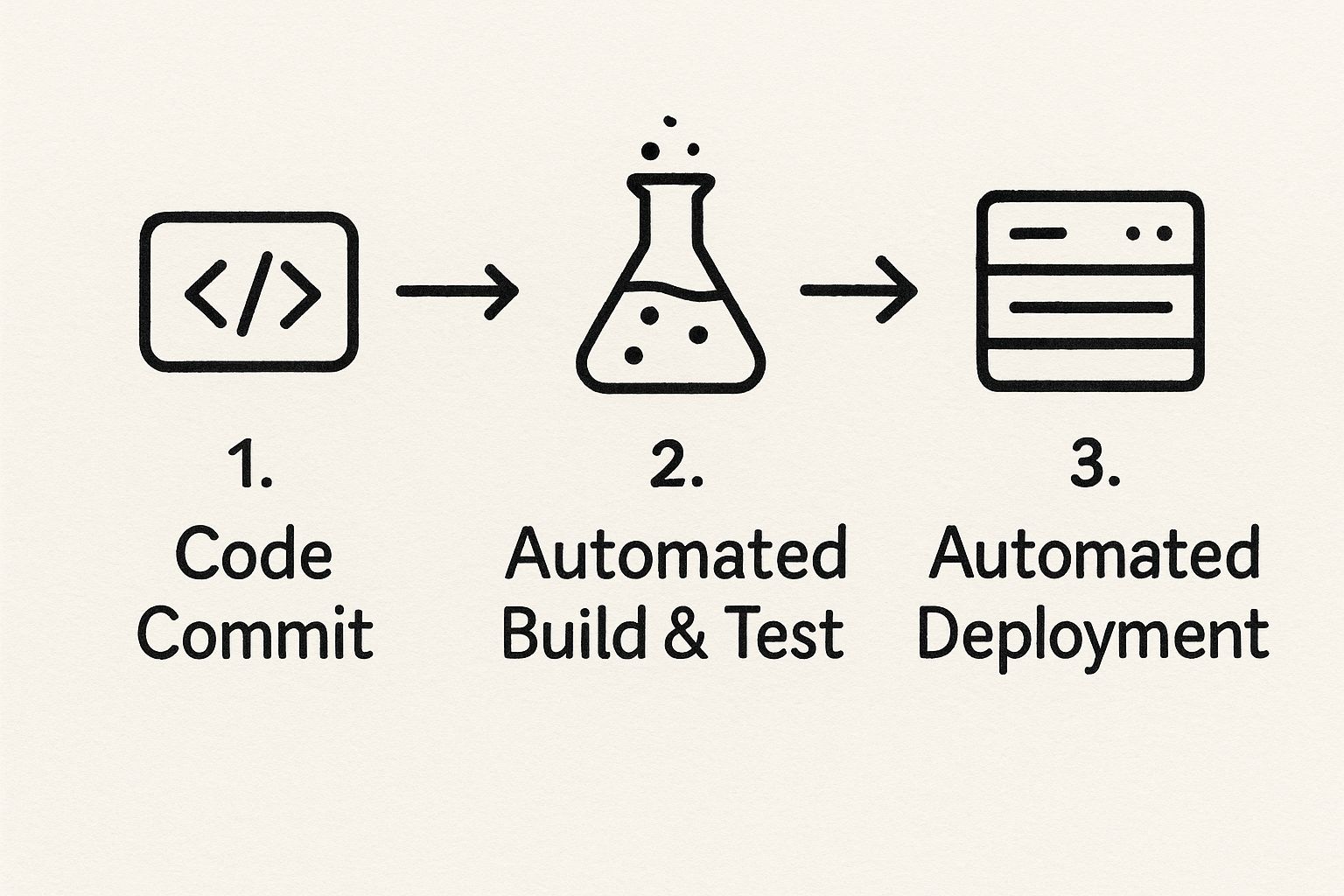
As you can see, each step acts as a gatekeeper, confirming quality before the code can move on.
Deploying the Artifact to Different Environments
With a validated artifact ready to go, the deployment server takes over. It pushes this artifact through a series of environments, each one serving a different purpose. Before getting too deep into the full deployment pipeline, it's good to understand its foundational parts, like Continuous Integration. For instance, a quick read on Continuous Integration (CI) for Flutter apps can shed light on these critical early stages.
A typical progression looks something like this:
- Testing/QA Environment: This is where automated end-to-end tests and more intense quality assurance checks happen.
- Staging Environment: Think of this as a near-perfect clone of production. It's the last stop for final validation and user acceptance testing.
- Production Environment: The live server. This is where real users interact with your application.
Each stage adds another layer of confidence. This entire system is usually part of a broader practice known as CI/CD. If you want to connect the dots, you can learn more about what a CI/CD pipeline is and see how all these automated steps fit together. This structured, stage-by-stage process turns what used to be risky, manual releases into a safe, predictable, and transparent routine.
The Real-World Benefits of Automating Deployments
Moving to deployment automation isn't just a technical tweak; it's a strategic move for the entire business, and the benefits show up almost immediately. The most obvious win is a massive boost in speed. Processes that used to gobble up weeks of meticulous planning and manual button-pushing can now be wrapped up in a few hours, or even minutes.
This kind of speed makes a business incredibly agile. Need to push a new feature? A critical bug fix? An urgent security patch? You can get it into the hands of your users almost instantly, giving you a serious leg up on the competition.
Reducing Risk and Boosting Reliability
Let's be honest: manual deployments are a minefield. A single typo in a command or a forgotten step can bring down a system, leading to lost revenue and eroding the trust you've built with your customers. Automation systematically pulls these human-error landmines out of the process.
When you codify your deployment pipeline, you guarantee that every single release is executed with perfect consistency. Automated tests and validation checks act as tireless gatekeepers, catching problems long before they ever see a production environment. In fact, organizations that embrace DevOps automation report a staggering 57% reduction in deployment failures.
The end result is a far more resilient and predictable delivery cycle. Instead of your team being on high alert for post-release fires, they can trust the pipeline to ship stable code every time.
A solid deployment automation strategy transforms releases from high-stakes gambles into low-risk, repeatable events. This stability frees up teams to focus on innovation instead of disaster recovery.
Empowering Engineers and Driving Innovation
Beyond all the technical gains, one of the biggest payoffs is the human one. When you free up highly skilled engineers from the soul-crushing grind of repetitive deployment tasks, you see an incredible shift in morale and creativity.
Developers who don't have to sweat the mechanics of a release can pour all their energy into what they're truly great at: solving tough problems and building amazing products. This simple change cultivates a culture of innovation, where teams feel safe to experiment and iterate quickly. It's also a key part of unlocking long-term savings in software development by making everyone more efficient.
This isn't just a niche idea anymore. The market for application release automation is expected to balloon to USD 12.84 billion by 2030, fueled by the shift to modern architectures and AI-driven predictive tools. At the end of the day, automation doesn't just make code better; it creates a more secure, efficient, and innovative environment for the people who write it.
Choosing the Right Tools for Your Automation Stack
Putting together a solid deployment automation pipeline is a lot like building a high-performance engine; every component needs to fit and work together perfectly. The modern DevOps world is full of specialized tools, each designed to solve a specific piece of the software delivery puzzle. It can feel a little overwhelming, but things get a lot clearer once you understand what each tool actually does.
The absolute heart of any automation stack is the CI/CD platform. Think of it as the conductor of your orchestra, coordinating the entire flow from the moment code is committed all the way to its final deployment. These platforms are the ones that trigger builds, run all your tests, and manage the release process.
H3: Orchestrators and Workflow Managers
Your CI/CD platform is the central nervous system of your entire deployment automation setup. It hooks directly into your version control system (like GitHub) and kicks off the whole sequence of events as soon as new code is pushed.
Some of the most popular choices you'll see are:
- GitHub Actions: This lets you build CI/CD pipelines right inside your code repository. It's a natural, seamless choice for any team already living in GitHub.
- GitLab CI/CD: Known for its "all-in-one" philosophy, GitLab bundles source code management, CI/CD, and a lot more into a single, integrated platform.
- Jenkins: As a highly extensible and open-source option, Jenkins is a true workhorse. You can customize it to handle just about any workflow you can dream up.
Picking the right platform is a huge first step. For a much deeper dive into the options out there, check out this guide to the best CI/CD tools for modern development.
H3: Environment and Configuration Management
Once you have an orchestrator, you need to make sure your server environments are consistent and repeatable. This is where configuration management and containerization tools come in to play, finally stamping out that classic "well, it worked on my machine" problem for good.
The big idea here is to treat your infrastructure like code. When you define server setups in version-controlled files, you create a single source of truth that guarantees every environment—from a developer's laptop to production—is absolutely identical.
Key tools in this category include:
- Ansible, Puppet, and Chef: These are the classic configuration management tools. They automate everything from installing software and running system updates to enforcing security policies across all your servers.
- Docker: This is the industry standard for containerization. It packages your application and all its dependencies into a lightweight, portable container that is guaranteed to run the same way everywhere.
- Kubernetes: When you start running a lot of containers, Kubernetes steps in as the orchestrator. It automates their deployment, scaling, and management so you don't have to.
To give you a clearer picture, here’s how these tool categories break down:
Key Deployment Automation Tool Categories
| Tool Category | Primary Function | Popular Examples |
|---|---|---|
| CI/CD Platforms | Orchestrate the entire build, test, and deploy workflow. | GitHub Actions, GitLab CI/CD, Jenkins |
| Configuration Management | Automate server setup, software installation, and policy enforcement. | Ansible, Puppet, Chef |
| Containerization | Package applications and dependencies into isolated, portable units. | Docker, Podman |
| Container Orchestration | Manage the lifecycle of containers at scale. | Kubernetes, Docker Swarm |
| Pull Request Automation | Automate checks and merges before code enters the main branch. | Mergify |
This table helps visualize how different tools tackle specific stages of the automation process, from initial code submission to large-scale production management.
Finally, don't forget that specialized tools can automate critical steps before the main pipeline even kicks off. A tool like Mergify, for instance, automates the entire pull request management process. It ensures code meets all quality and security standards before it gets merged, acting as a gatekeeper for your main branch. This kind of pre-emptive quality control strengthens the entire automation chain, making your eventual deployments that much more reliable.
Navigating the Bumps in the Road to Automation
Let's be real: moving to full deployment automation isn't like flipping a switch. It's a journey. And like any worthwhile journey, it has its share of predictable challenges that can throw you off course if you’re not ready for them.
The biggest hurdle, and the one that surprises most teams, is cultural, not technical. True automation lives and breathes the DevOps philosophy, which means tearing down the old walls between development and operations. If your Dev and Ops teams are still operating in their own little worlds with their own separate goals, your shiny new automation pipeline will quickly become a source of friction instead of a bridge.
The Challenge of Legacy Systems
Another all-too-common roadblock is wrestling with legacy systems. Many older applications simply weren't built for the fast-paced, API-driven world of modern CI/CD. They might be missing proper testing frameworks, have configurations hard-coded right into the source, or rely on manual deployment steps that are a nightmare to script.
Trying to retrofit these old-school systems for an automated pipeline can feel a bit like installing a smart-home system in a historic landmark. It’s definitely possible, but it demands careful planning and some clever workarounds to get the job done without breaking what's already there.
Overcoming the Learning Curve
Finally, you can't ignore the learning curve. Bringing in a new stack of tools—whether it's a CI/CD platform like GitHub Actions or container orchestration with Kubernetes—means your teams need to learn new skills. Without good training and support, developers and operations engineers can easily get overwhelmed, leading to slow adoption or, even worse, doing things the wrong way.
But for the teams that push through, the payoff is huge. Data shows that integrating DevOps automation can slash deployment failures by a massive 57%. That alone makes navigating these initial bumps worth the effort.
To build momentum without getting bogged down, try these moves:
- Start Small: Don't try to boil the ocean. Pick a single, low-risk project or service to pilot your new process.
- Iterate and Improve: Take what you learned from that first project and use it to refine your approach before you move on to more critical applications.
- Provide Resources: Invest in solid training and clear documentation. Give your team the tools they need to get comfortable with the new way of working.
The trick is to treat the implementation of deployment automation like an iterative development project in itself. Start with a manageable scope, build on small wins, and create a sustainable path toward a much more efficient and reliable way to ship software.
Your First Steps into Automated Deployment
Jumping into deployment automation can feel like a huge project, but the secret is to start small and build from there. You don't need a flawless, all-in-one pipeline from day one. Instead, focus on small, manageable steps that give you real wins and build your team's confidence.
The absolute bedrock of any automated workflow is solid version control. If you’re not using a system like Git, stop everything and do that first. It’s your single source of truth for your code, tracking every change and making the whole process transparent and easy to follow.
Building Your First Pipeline
With version control sorted, your next move is to pick a simple CI/CD tool. Platforms like GitHub Actions or GitLab CI are great places to start because they live right inside your repositories, which cuts down on setup headaches.
Your first goal? An automated build. This just means telling your CI/CD tool to automatically compile your code and run tests every time someone pushes a change. This one step gives you immediate feedback, catching errors just minutes after they’re introduced.
Think of this as your first victory. It proves the concept by creating a safety net that confirms your app can at least build successfully after every change. It’s a simple starting point, but it's powerful.
From Building to Deploying
Once you have a reliable automated build, the next milestone is to script a basic deployment. The key here is to aim for a safe, non-production environment, like a testing or staging server. The script doesn't need to be fancy—it can just be a few commands that copy the built app to the server and restart whatever services are needed.
This is a critical step because it closes the loop between building code and actually seeing it run somewhere. As you get more comfortable with this, you can start adding more sophisticated automated tests to check if the deployment worked, which builds even more trust in your pipeline.
This step-by-step approach is becoming more common for businesses of all sizes. While big companies have historically led the charge in automation, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are now the fastest-growing group. This is mostly thanks to the rise of affordable automation tools built for smaller teams. You can dive deeper into this market shift in this industry analysis on GrandviewResearch.com.
Remember, the goal is progress, not perfection. Each small step—from version control to an automated build to a scripted deployment—cuts down on manual work and reduces risk. By improving your pipeline little by little, you build a solid system that turns software delivery from a stressful all-hands-on-deck event into a boring, predictable process.
Common Questions About Deployment Automation
When teams first start digging into deployment automation, a few questions always pop up. Getting these concepts straight is key to a smooth rollout.
Let's clear up one of the most common points of confusion: Continuous Delivery vs. Continuous Deployment. They sound similar, but the difference is huge. Continuous Delivery means your code is always ready to go—tested, packaged, and sitting on the tarmac—but a human has to give the final "go-live" command.
Continuous Deployment takes it a step further. It's the full-throttle version where every single change that passes all the automated checks gets pushed directly to your users. No human intervention needed.
Does Automation Actually Improve Code Quality?
Yes, without a doubt. Think of an automated pipeline as a relentless quality inspector who never gets tired. By forcing every single commit to run through a gauntlet of automated tests, code analysis, and security scans, it catches bugs and vulnerabilities right away.
This systematic approach stops bad code from ever making it into production. The results speak for themselves: organizations that get this right often see a 57% reduction in deployment failures.
What Skills Are Essential for Success?
You don't need a team of wizards, but a few core skills are non-negotiable.
First, everyone needs to be rock-solid with version control, especially Git. Beyond that, some basic scripting knowledge for writing deployment jobs and a good grasp of testing principles are crucial.
But the real secret sauce? It’s the culture. A collaborative, DevOps mindset is the glue that holds everything together and makes the tools truly work.
Ready to automate your pull requests and secure your CI/CD pipeline? Mergify ensures your code is always ready for deployment by automating merges, backports, and updates. Stop wasting time on manual tasks and start shipping faster. Learn more at https://mergify.com.